Brand Equity Meaning
Brand equity refers to the intangible value and worth that a brand possesses in the eyes of consumers and the market. It represents the overall perception, reputation, and recognition that a brand has established over time.
Brand equity encompasses various aspects such as brand awareness, brand associations, perceived quality, and brand loyalty. Essentially, it reflects the strength and value of a brand in relation to its competitors.
Importance of Brand Equity
Brand equity plays a pivotal role in today’s highly competitive business landscape. It goes beyond the tangible assets and products of a company, shaping how consumers perceive and connect with the brand. The significance of brand equity can be summarized in the following points:
1. Differentiation
Building brand equity allows businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors. It helps create a unique position in the market, enabling consumers to distinguish and prefer the brand over others.
2. Customer Loyalty
Strong brand equity cultivates customer loyalty. When consumers have positive associations and experiences with a brand, they are more likely to become repeat customers and advocate for the brand, leading to increased sales and market share.
3. Premium Pricing
Brands with high equity can command premium prices for their products or services. Customers are often willing to pay more for brands they perceive as trustworthy, reliable, and of superior quality, further boosting profitability.
4. Extension Opportunities
Strong brand equity opens doors for brand extensions. When consumers have a positive perception of a brand, they are more likely to embrace new offerings from the same brand, facilitating expansion into new product categories or markets.
5. Resilience during Crisis
Brands with established equity tend to fare better during challenging times. They possess a reservoir of goodwill and trust that can help navigate through crises, maintaining customer loyalty and mitigating potential damage to the brand’s reputation.
Components of Brand Equity
Brand equity, a key concept in marketing, refers to the value and strength of a brand in the eyes of consumers and the market.
It represents the accumulated perceptions, experiences, and associations that consumers have with a particular brand. Brand equity comprises several interrelated components that contribute to its overall value:
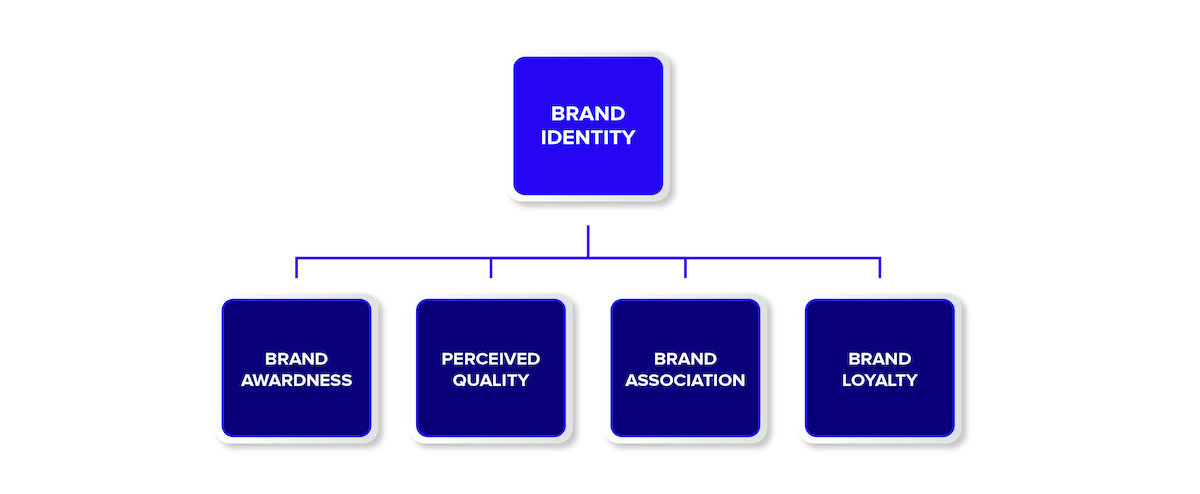
1. Brand Awareness
Brand awareness refers to the level of recognition and familiarity that consumers have with a brand. It indicates the extent to which a brand is known and remembered by its target audience. Strong brand awareness helps in capturing consumer attention, increasing the likelihood of consideration and purchase.
2. Brand Associations
Brand associations are the mental connections and attributes linked to a brand. They can be tangible (e.g., logo, tagline) or intangible (e.g., emotions, values). Positive brand associations help in building a favorable image and perception of the brand, influencing consumer preferences and decision-making.
3. Perceived Quality
Perceived quality refers to the consumer’s perception of the overall excellence, reliability, and superiority of a brand’s products or services. It encompasses factors such as functionality, performance, durability, and consistency. A brand with a strong reputation for high perceived quality gains consumer trust and loyalty.
4. Brand Loyalty
Brand loyalty represents the degree of commitment, attachment, and repeat purchases exhibited by consumers towards a specific brand.
It reflects the preference and trust consumers have in a brand, leading to repeat business and a higher customer lifetime value. Strong brand loyalty contributes to sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Understanding these components is crucial for comprehending the intricacies of brand equity. Together, they shape the perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors of consumers towards a brand.
Brand Equity Model
Brand equity models provide frameworks and approaches to understand and manage brand equity effectively.
Two widely recognized models in the field of marketing are the Keller Customer-Based Brand Equity Model and the Aaker Customer-Based Brand Equity Model.
Let’s explore these models and understand their key components and differences.
Keller Customer-Based Brand Equity Model
The Keller Customer-Based Brand Equity Model, developed by Kevin Lane Keller, emphasizes the importance of customer perceptions and experiences in building strong brand equity.
This model consists of four key components:
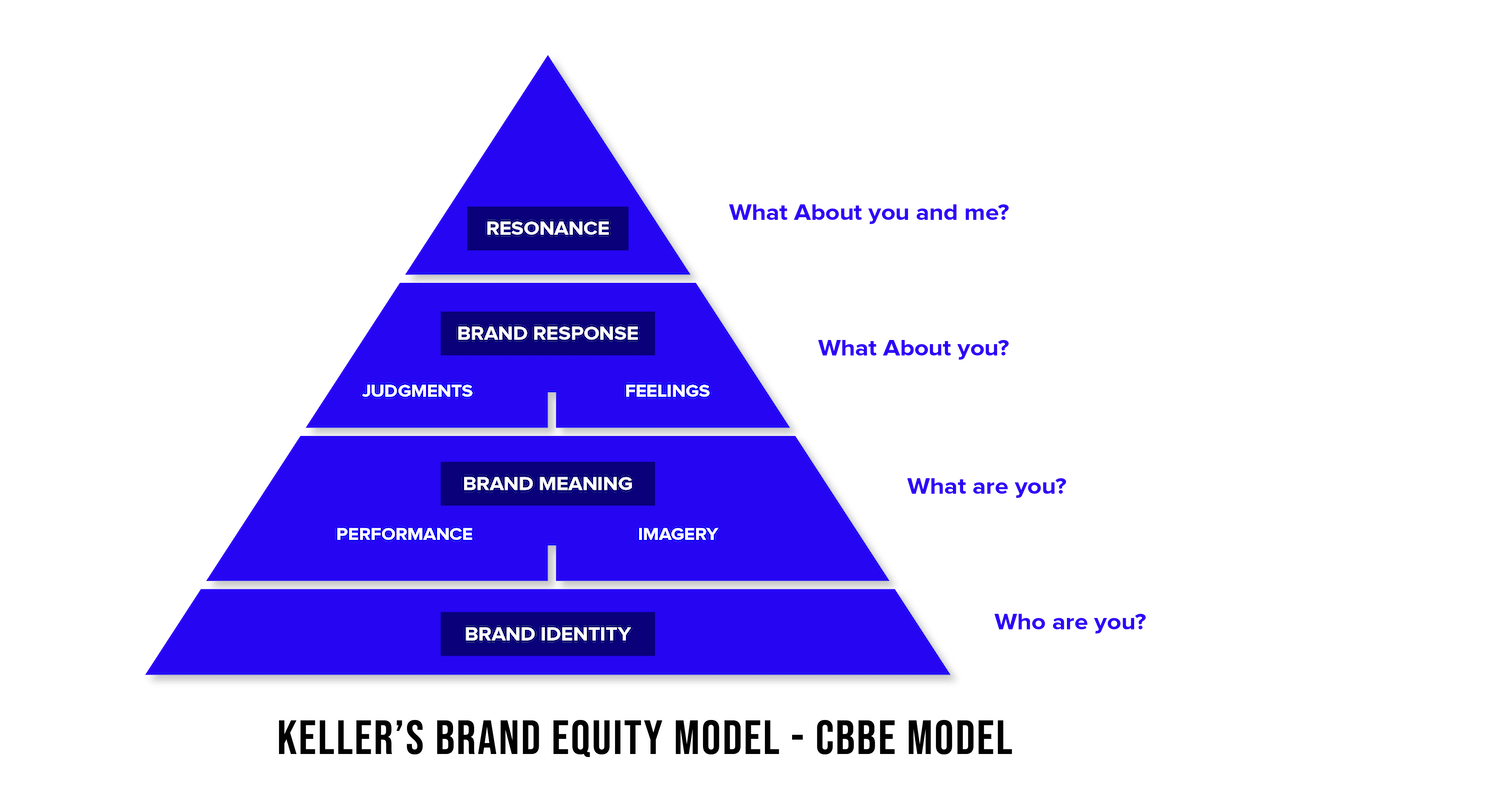
1. Brand Salience:
Brand salience refers to the level of brand awareness and recognition in the minds of customers. It includes aspects such as brand recall, brand familiarity, and the ability to evoke positive associations.
2. Brand Performance:
Brand performance assesses how well a brand meets customer expectations and delivers on its promised benefits. It considers factors such as product quality, reliability, and functionality.
3. Brand Imagery:
Brand imagery focuses on the associations and perceptions that customers have about a brand. It includes both tangible attributes (e.g., logo, packaging) and intangible aspects (e.g., brand personality, values).
4. Brand Judgments and Feelings:
Brand judgments and feelings represent the overall customer evaluations and emotional responses towards a brand.
This component includes factors such as perceived quality, brand credibility, and brand likability.
Aaker Customer-Based Brand Equity Model
The Aaker Customer-Based Brand Equity Model, developed by David Aaker, takes a broader perspective on brand equity and considers both customer perceptions and brand identity.
This model comprises five key components:
1. Brand Identity:
Brand identity focuses on the unique set of brand associations, values, and personality traits that differentiate a brand from its competitors.
It includes aspects such as brand vision, mission, and positioning.
2. Brand Meaning:
Brand meaning encompasses the functional and symbolic benefits associated with a brand. It explores how customers interpret and derive value from the brand beyond its basic features and attributes.
3. Brand Response:
Brand response evaluates how customers perceive and respond to the brand. It includes factors such as brand preference, brand loyalty, and the likelihood of recommending the brand to others.
4. Brand Relationships:
Brand relationships delve into the emotional connections and interactions that customers have with the brand. It explores aspects such as trust, attachment, and engagement with the brand.
5. Brand Resonance:
Brand resonance represents the ultimate level of brand loyalty and customer engagement. It reflects the depth of the relationship between customers and the brand, leading to a sense of community and active involvement.
While both models share a customer-centric approach, the Keller model focuses more on customer perceptions and experiences, while the Aaker model incorporates brand identity and meaning.
The choice of which model to adopt depends on the specific needs and objectives of a brand.
Successful Brands with High Brand Equity
To understand the practical implications of brand equity, let’s explore a few case studies of brands that have successfully built and maintained high levels of brand equity:
1. Apple
Apple is a prime example of a brand with exceptional brand equity. Through innovative products, sleek designs, and a customer-centric approach, Apple has established itself as a leader in the technology industry.
The Apple brand is synonymous with quality, innovation, and user experience. Apple’s brand equity is evident in its loyal customer base, strong brand associations with creativity and simplicity, and its ability to command premium prices.
2. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, one of the world’s most recognizable brands, has built a remarkable level of brand equity over its long history. Through consistent branding, iconic advertisements, and emotional connections, Coca-Cola has created a powerful brand identity.
The brand is associated with happiness, joy, and shared moments. Coca-Cola’s brand equity is reflected in its strong global presence, high brand recognition, and enduring customer loyalty.
3. Nike
Nike, a prominent sportswear brand, has successfully established a strong brand equity through its strategic marketing and brand positioning.
Nike’s brand is associated with performance, athleticism, and empowerment. By collaborating with athletes, sponsoring major sports events, and delivering high-quality products,
Nike has cultivated a loyal customer base and strong brand loyalty. Nike’s brand equity is evident in its market dominance, strong brand associations, and its ability to influence consumer behavior.
4. Starbucks
Starbucks, a leading coffeehouse chain, has built a distinct brand equity centered around the coffee experience. With a focus on premium quality, personalized service, and creating a welcoming environment, Starbucks has created a strong emotional connection with its customers.
Starbucks’ brand equity is demonstrated by its loyal customer base, widespread global presence, and the association of the brand with a premium coffee culture.
These case studies highlight the strategies employed by successful brands to build and maintain high levels of brand equity.
Through consistent branding, delivering exceptional customer experiences, and establishing strong brand associations, these brands have successfully differentiated themselves and created long-lasting relationships with their customers.
By studying these brands, businesses can gain valuable insights and inspiration for their own brand equity endeavors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, brand equity is crucial for the success of a brand, representing its value and relationship with consumers.
Through components like awareness, associations, quality, and loyalty, brands can build a strong equity. Successful brands like Apple, Coca-Cola, Nike, and Starbucks exemplify the power of brand equity. Measuring it through quantitative and qualitative methods provides valuable insights.
So, if you’re ready to take your brand to the next level and boost its equity, I encourage you to contact Neu Entity. Let’s embark on a journey together to create a powerful brand that leaves a lasting impression.
Reach out to us today, and let’s start transforming your brand’s equity into real business success.
Related Articles
Let’s Talk!
If what you see here is relevant for you and can help you grow your business or organisation, we’d love to discuss further with you. Drop us a message or schedule an appointment with us.